In today’s manufacturing landscape, the ability to create complex and precise parts quickly and efficiently is crucial. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining stands at the forefront of these capabilities, offering automated and highly accurate material removal processes. This article delves into the intricacies of Usinage CNC, including its processes, materials, applications, benefits, and limitations.
Qu'est-ce que l'usinage CNC ?
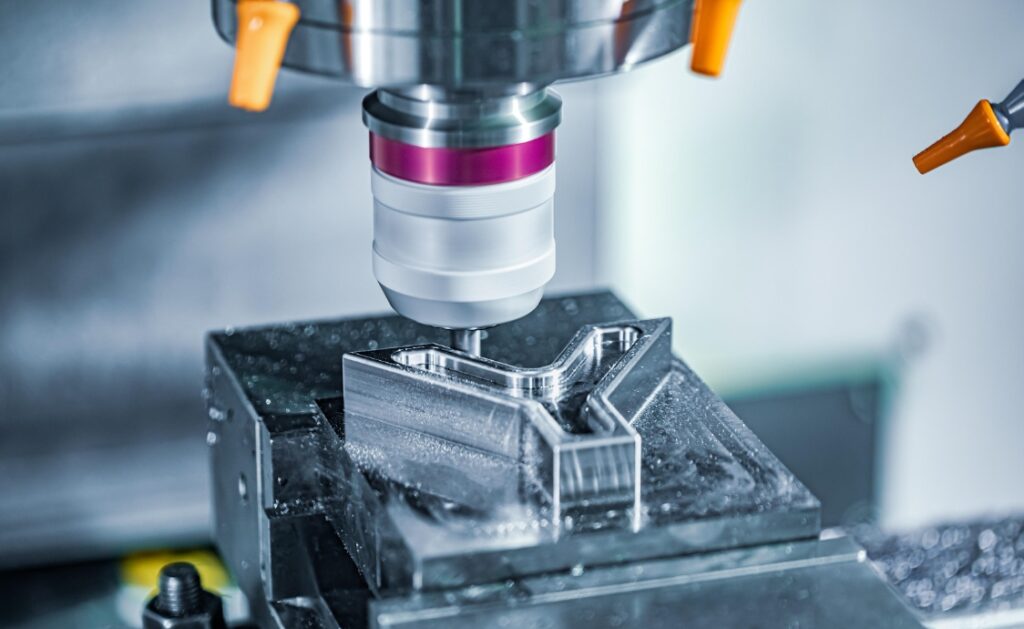
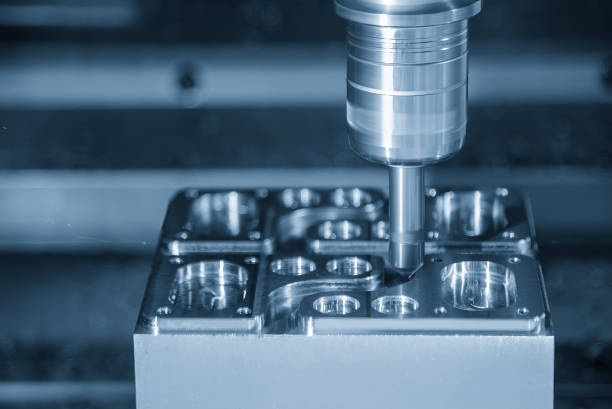
CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that employs computer-controlled machines to remove material from raw stock, shaping it into desired components. This process is governed by a set of computer-generated instructions, known as G-codes, which guide the machine’s movements and operations. CNC machining is applicable to a wide range of materials, from metals and plastics to wood and composites, making it a versatile solution for various industries.

Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines are categorized based on their specific functions and the type of operations they perform. Here are the main types of CNC machines used in precision machining:
- Machines à fraiser CNC:
- Function: Utilize rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece.
- Applications: Suitable for creating complex shapes, slots, holes, and features in a workpiece.
- Avantages: High versatility, capable of handling a variety of materials and geometries.
- CNC Turning Machines:
- Function: Rotate the workpiece against a stationary cutting tool.
- Applications: Ideal for producing cylindrical parts such as shafts and bushings.
- Avantages: High precision in producing symmetrical parts.
- Machines à rectifier CNC:
- Function: Use abrasive wheels to achieve high surface quality and fine finishes.
- Applications: Commonly used for finishing operations to achieve tight tolerances.
- Avantages: Excellent for high-precision finishing of hardened materials.
- Usinage par décharge électrique (EDM):
- Function: Use electrical discharges to erode material from the workpiece.
- Applications: Suitable for hard materials and complex geometries.
- Avantages: Can machine materials that are difficult to process with conventional methods.
- Multi-axis CNC Machines:
- Function: Provide movement in multiple axes, allowing for complex part geometries.
- Applications: Essential for aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
- Avantages: Capable of producing intricate and detailed components with minimal setup changes.

How Does CNC Machining Work?
The Processus d'usinage CNC involves several key steps to ensure precision and accuracy in manufacturing parts:
1. Designing the CAD Model
The process begins with creating a detailed 3D model of the part using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This model serves as the blueprint for the CNC machine, defining the dimensions, features, and tolerances required for the final part.
2. Converting the CAD File to a CNC Program
Once the CAD model is complete, it is converted into a set of instructions for the CNC machine using CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software. This conversion process generates G-codes and M-codes, which provide the machine with the necessary coordinates and commands to execute the machining operations.

3. Preparing the CNC Machine
Before machining can begin, the CNC machine must be properly set up. This involves securing the raw stock material, selecting the appropriate cutting tools, and calibrating the machine. Advanced CNC machines may have automatic tool changers and tool libraries to streamline this process.
4. Executing the Machining Operation
With the setup complete, the machining operation can commence. The CNC machine follows the programmed instructions to move the cutting tool and remove material from the workpiece, shaping it into the desired form. Depending on the complexity of the part, multiple tools and orientations may be required.

5. Post-Machining Processes
After the machining operation, the part may undergo additional processes such as grinding, polishing, or heat treatment to achieve the final specifications. These secondary processes ensure that the part meets the required surface quality and dimensional accuracy.
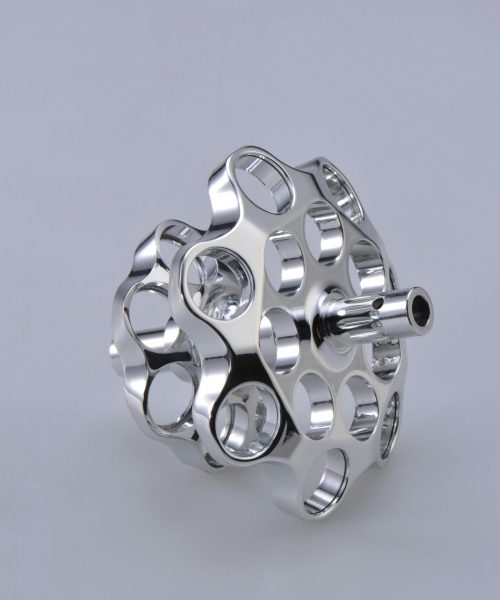
Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machining can be applied to a wide variety of materials, each with its own unique properties and machining requirements. Here are some of the most commonly used materials in CNC machining:
1. Metals
- Types: Aluminum, steel, stainless steel, titanium, brass, copper, and nickel superalloys.
- Applications: Engine components, aerospace parts, medical devices, and structural components.
- Avantages: High strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
2. Plastics
- Types: ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), nylon, polycarbonate, and POM (Polyoxymethylene).
- Applications: Valve bodies, bushings, and prototypes for injection molding.
- Avantages: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to machine.
3. Wood
- Types: Various hardwoods and softwoods.
- Applications: Furniture, decorative panels, and window frames.
- Avantages: Easily machinable and ideal for decorative and structural applications.
4. Foams
- Types: Polyurethane foam, expanded polystyrene, and closed-cell foam.
- Applications: Packaging, insulation, and prototypes.
- Avantages: Lightweight, easy to cut, and excellent for cushioning and insulation.
5. Composites
- Types: Fiberglass, carbon fiber, and aramid composites.
- Applications: Aerospace components, marine parts, and sports equipment.
- Avantages: High strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and excellent mechanical properties.

Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is employed across numerous industries due to its versatility and precision. Here are some of the key applications:
1. Aerospace Industry
In the aerospace sector, CNC machining is crucial for producing high-precision components such as turbine blades, engine parts, and structural elements. The stringent quality standards and material requirements in aerospace make CNC machining an ideal solution.
2. Automotive Manufacturing
CNC machining is widely used in the automotive industry to manufacture engine components, transmission parts, and chassis elements. The ability to produce high-precision parts ensures optimal performance and reliability in vehicles.
3. Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical industry relies on CNC machining for producing surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. The precision and cleanliness standards required in medical device manufacturing make CNC machining indispensable.
4. Electronics and Semiconductor Industry
In electronics manufacturing, CNC machining is used to create components for consumer electronics, semiconductors, and telecommunications equipment. The precision and consistency of CNC machining ensure reliability and functionality in electronic products.
5. Defense and Military Applications
CNC machining is employed in the defense sector to produce components for weaponry, radar systems, and armored vehicles. The durability, accuracy, and adherence to specifications make CNC machining essential for defense applications.
6. Renewable Energy Sector
Les composants des technologies d'énergie renouvelable telles que les éoliennes, les panneaux solaires et les systèmes de stockage d'énergie nécessitent un usinage de précision pour garantir leur efficacité et leur longévité. L'usinage CNC permet de produire des composants de haute performance essentiels à l'infrastructure des énergies renouvelables.

Avantages de l'usinage CNC
The adoption of CNC machining offers numerous advantages over traditional machining methods, making it indispensable in modern manufacturing environments. Here are some key benefits:
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Repeatability
Les machines CNC fonctionnent avec une précision de l'ordre du micron, ce qui garantit que chaque pièce produite répond de manière répétée aux spécifications dimensionnelles exactes. Cette constance réduit la variabilité et améliore la qualité du produit.
2. Increased Productivity and Efficiency
L'automatisation de l'usinage CNC permet d'accélérer les temps de cycle et d'augmenter le rendement par rapport aux opérations manuelles. Ces gains d'efficacité se traduisent par une réduction des délais et une amélioration de la capacité de production.
3. Versatility in Material Compatibility
L'usinage de précision CNC prend en charge une large gamme de matériaux, y compris les métaux (aluminium, acier inoxydable, titane), les plastiques (ABS, POM) et les composites. Cette polyvalence lui permet de s'adapter à diverses applications industrielles.
4. Complex Geometry Capability
Grâce à leurs capacités d'usinage multi-axes, les machines CNC peuvent créer des géométries et des caractéristiques complexes qu'il est difficile, voire impossible, d'obtenir avec les méthodes d'usinage conventionnelles. Cette capacité est cruciale pour la conception de produits innovants.
5. Cost-effectiveness
Malgré les coûts d'installation initiaux, l'usinage de précision CNC permet de réaliser des économies à long terme grâce à la réduction des rebuts, à la diminution des coûts de main-d'œuvre et à la minimisation des besoins en matière d'opérations secondaires. Il optimise l'utilisation des ressources et améliore la rentabilité.
6. Improved Safety
The automation inherent in CNC machining reduces the need for manual intervention, minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries. Operators can focus on overseeing the process and performing quality checks, rather than handling the machining directly.
7. Scalability
CNC machining is highly scalable, making it suitable for both small batch production and large-scale manufacturing. This flexibility allows businesses to adapt to changing production demands without significant adjustments to the process.

Limitations of CNC Machining
While CNC machining offers numerous advantages, it also has some limitations:
1. High Initial Investment
CNC machines and the required software can be expensive, making the initial investment significant. This cost must be justified by the expected production volumes and potential return on investment.
2. Specialized Skills Required
Operating and programming CNC machines require specialized skills and knowledge. Skilled operators and programmers are essential to ensure efficient and accurate machining operations.
3. Material Waste
As a subtractive manufacturing process, CNC machining inherently generates waste material. Managing and recycling this waste is important for environmental sustainability and cost management.
Cost Factors in CNC Machining
The cost of CNC machining a part depends on several factors, including:
1. Material
Some materials are cheaper and easier to process with CNC machines than others. For example, machining aluminum is generally less expensive than machining nickel superalloys due to differences in tool wear and cutting speeds.
2. Complexity
The complexity of the part significantly affects the cost. Parts with intricate features and complex geometries require more machining time and sophisticated tooling, increasing the overall cost.
3. Tolerances
Tighter tolerances demand higher precision and more careful machining, leading to increased costs. Specifying unnecessarily tight tolerances on non-critical features can drive up expenses.
4. Surface Finish
Achieving high-quality surface finishes often requires specialized tooling and additional machining time, contributing to higher costs.
5. Quantity
Low-volume production typically incurs higher costs per part due to setup and programming expenses being spread over fewer units. High-volume production benefits from economies of scale, reducing the cost per part.
Choosing a CNC Machining Service Provider
Selecting the right Service d'usinage CNC provider is crucial for achieving optimal manufacturing outcomes. Consider the following factors when choosing a machining partner:
1. Expertise and Experience
Recherchez un fournisseur qui possède une vaste expérience de l'usinage de précision CNC et qui a fait ses preuves en matière de livraison de pièces de haute qualité dans divers secteurs d'activité. Une expertise dans le traitement de géométries et de matériaux complexes est un atout.
2. Technological Capabilities
Évaluez les capacités d'usinage du fournisseur, notamment les types de machines à commande numérique, les capacités multi-axes et la maîtrise des logiciels de CAO/FAO. Les technologies de pointe permettent une production efficace et le respect de tolérances strictes.
3. Quality Assurance Standards
Veillez à ce que le fournisseur de services d'usinage respecte des mesures de contrôle de la qualité rigoureuses et des certifications telles que la norme ISO 9001. Les processus d'assurance qualité réduisent les risques de défauts et garantissent que chaque pièce répond aux exigences spécifiées.
4. Customization and Flexibility
Choisissez un partenaire d'usinage capable de répondre à des exigences personnalisées et à des besoins de prototypage rapide. La flexibilité des volumes de production et de la programmation permet de répondre aux fluctuations de la demande et des délais des projets.
5. Value-added Services
Évaluez les services supplémentaires proposés par le fournisseur d'usinage, tels que la finition, l'assemblage et le soutien logistique. Des services complets permettent de rationaliser la chaîne d'approvisionnement et d'améliorer l'efficacité globale du projet.

Conclusion
Les services d'usinage de précision CNC représentent le summum de l'excellence en matière de fabrication. Ils associent des technologies de pointe à un savoir-faire méticuleux pour produire des pièces et des composants de qualité supérieure. À mesure que les industries continuent d'évoluer, la demande de précision, de fiabilité et d'innovation dans les processus de fabrication ne fera que croître. En tirant parti de l'usinage de précision CNC, les entreprises peuvent réaliser des gains d'efficacité opérationnelle, accélérer les délais de mise sur le marché et conserver des avantages concurrentiels sur un marché mondial axé sur la qualité et la précision.
En résumé, l'intégration des services d'usinage de précision CNC dans les opérations de fabrication permet aux industries de repousser les limites du possible, de stimuler l'innovation et de façonner l'avenir de la fabrication dans le monde entier.
Questions fréquemment posées
1. What is the difference between precision machining and non-precision machining?
Precision machining is designed for tight tolerances, producing parts with greater accuracy, high repeatability, and lower defect rates. Non-precision machining does not require the same level of precision and is used for less critical applications.
2. What are precision machine parts?
Precision machine parts are created with specialized tools and equipment to meet the original design with high accuracy. These parts can be made from metals, alloys, plastics, and other materials.
3. What are precision machine components?
Precision machine components are made with special tools and processes controlled by CNC technology. These processes commonly involve CNC machining mills, drills, turners, laser cutters, EDM cutters, and grinders.
4. What is high precision machining?
High precision machining, or high precision CNC machining, uses CNC machines to create parts with very high accuracy. The parts are designed based on Computer-Aided Design (CAD) blueprints and are machined to tight tolerances.

Get Started with GCH PROCESS
Experience the precision and reliability of GCH PROCESS. Contact us today to discuss your Usinage CNC needs, request a quote, and discover how we can support your manufacturing goals with superior precision and efficiency.