Introducción
Injection molding services have become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, providing companies with the ability to produce high-quality, complex parts at scale. This manufacturing process is widely used across various industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, medical devices, and consumer goods, enabling the production of millions of identical parts with precision and consistency. In this article, we will explore the essential aspects of injection molding services, from the process itself to the materials used, the benefits and challenges, and the future of this critical manufacturing technology.

Understanding the Injection Molding Process
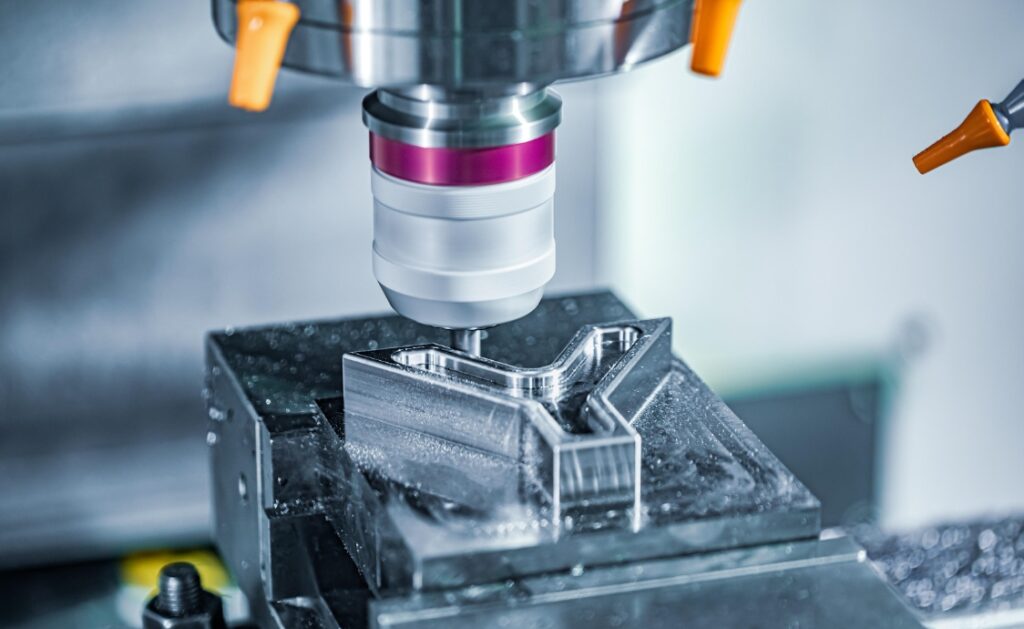
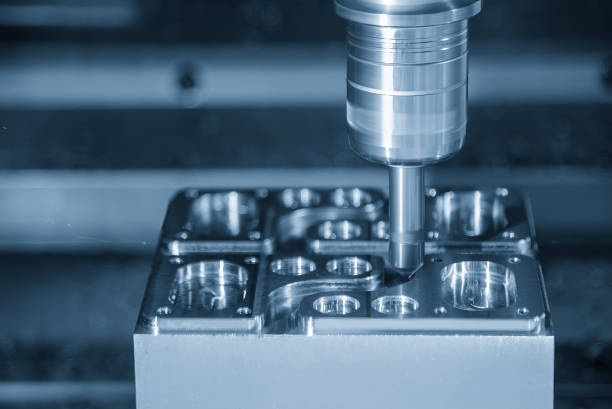
Injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten material is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure. The material then cools and solidifies, taking the shape of the mold to form the final part. The process is highly efficient and can produce large volumes of parts with minimal variation, making it ideal for mass production.
The Injection Molding Machine
The injection molding machine is the heart of the process, consisting of three main components: the injection unit, the mold, and the clamping unit.
Injection Unit: The injection unit is responsible for melting the raw material and injecting it into the mold cavity. The unit includes a hopper where the material is fed, a barrel where it is heated, and a screw that moves the molten material into the mold.
Mold: The mold is the part of the machine where the molten material is shaped into the final part. It is typically made of steel or aluminum and consists of two halves that come together to form the mold cavity.
Clamping Unit: The clamping unit holds the mold in place and ensures that it remains closed during the injection process. After the part has cooled and solidified, the clamping unit opens the mold to eject the finished part.

The Injection Molding Cycle
The injection molding cycle consists of several steps, each crucial to the success of the process:
Clamping: The mold halves are clamped together, creating a sealed cavity ready for injection.
Injection: The molten material is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure, ensuring it fills the entire cavity and takes the shape of the mold.
Cooling: Once the material has filled the cavity, it begins to cool and solidify. Cooling is a critical step, as it determines the final properties and quality of the part.
Ejection: After the part has cooled and solidified, the mold opens, and the part is ejected.
Cycle Time: The total cycle time can vary depending on the size and complexity of the part, the material used, and the cooling time. Typical cycle times range from a few seconds to several minutes.

Materials Used in Injection Molding Services
One of the key advantages of injection molding services is the wide range of materials that can be used. Each material offers different properties, making it suitable for various applications.
Termoplásticos
Thermoplastics are the most common materials used in injection molding. They can be melted and re-melted without significant degradation, making them versatile and cost-effective.
Polyethylene (PE): Known for its flexibility and chemical resistance, polyethylene is widely used in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
Polypropylene (PP): Polypropylene is valued for its strength, stiffness, and resistance to chemicals and fatigue, making it ideal for automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer products.
Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): ABS is a tough, impact-resistant plastic commonly used in automotive parts, electronics, and household appliances.
Polycarbonate (PC): Polycarbonate is known for its toughness and transparency, making it suitable for automotive lighting, optical lenses, and medical devices.

Thermosets
Thermosets undergo a chemical reaction during molding that creates a rigid structure. Once set, they cannot be re-melted, offering excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability.
Epoxy: Epoxy is used in coatings, adhesives, and electrical components due to its excellent mechanical properties and chemical resistance.
Phenolic Resins: Known for their heat resistance and electrical insulating properties, phenolic resins are used in electrical components and automotive parts.
Elastomers
Elastomers are materials known for their flexibility and ability to return to their original shape after deformation.
Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): Combining the properties of thermoplastics and elastomers, TPEs are used in automotive parts, medical devices, and consumer goods.
Silicone: Silicone is valued for its flexibility and heat resistance, making it ideal for seals, gaskets, and medical devices.
Specialty Materials
Beyond traditional plastics and elastomers, injection molding services also work with specialty materials, including metal injection molding (MIM) and ceramic injection molding (CIM).
Metal Injection Molding (MIM): MIM combines injection molding with powder metallurgy to create complex metal parts used in automotive, aerospace, and medical devices.
Ceramic Injection Molding (CIM): CIM is used to produce high-precision ceramic parts for applications requiring high wear resistance, such as aerospace and electronics.

Benefits of Injection Molding Services
Injection molding services offer several advantages that make them a popular choice for manufacturing across various industries.
High Efficiency and Production Speed
Injection molding is highly efficient, allowing for the rapid production of large volumes of parts. The process is automated, reducing labor costs and cycle times. Once the initial setup is complete, parts can be produced quickly, making injection molding ideal for mass production.
Consistency and Precision
Injection molding offers excellent consistency and precision, ensuring that each part is identical to the next. This consistency is crucial in industries like automotive and medical devices, where even minor deviations can affect performance and safety.
Design Flexibility
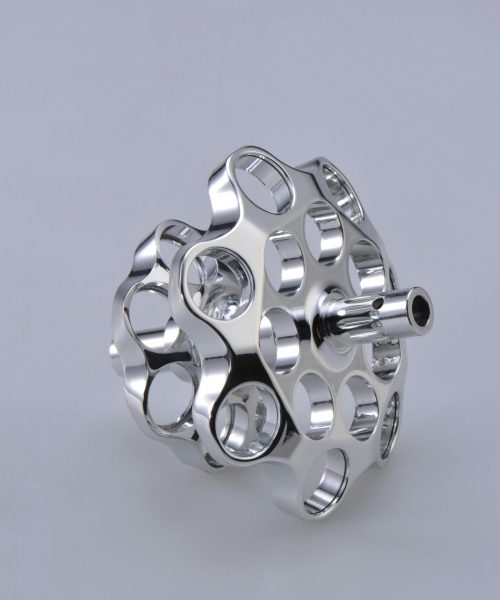
Injection molding provides significant design flexibility, allowing for the production of complex shapes and intricate details. The use of multi-cavity molds enables the simultaneous production of multiple parts, further enhancing efficiency.
Versatilidad de materiales
The wide range of materials available for injection molding allows manufacturers to choose the best material for their specific application. Whether it’s the strength of polypropylene, the clarity of polycarbonate, or the flexibility of TPE, injection molding services can meet diverse material requirements.
Reducción de residuos
Injection molding generates minimal waste, as excess material can often be recycled and reused. This efficiency makes injection molding a cost-effective and environmentally friendly manufacturing process.
Escalabilidad
Injection molding is highly scalable, making it suitable for both small and large production runs. The process can be adjusted to produce anything from a few hundred parts to millions, providing flexibility for manufacturers.
Challenges in Injection Molding Services
While injection molding services offer many benefits, they are not without challenges. These challenges must be carefully managed to ensure successful production.
High Initial Costs
The upfront costs of injection molding can be high, particularly for the design and fabrication of molds. This initial investment is justified by the long-term efficiency and cost savings in high-volume production, but it can be a barrier for small businesses or startups.
Selección de materiales
Choosing the right material for injection molding is critical to the success of the final product. Each material has specific properties that must align with the part’s requirements, including strength, flexibility, chemical resistance, and cost. Incorrect material selection can lead to part failure or performance issues.
Mold Design and Maintenance
The design of the mold is crucial to the success of the injection molding process. Poorly designed molds can lead to defects such as warping, sink marks, or flash. Additionally, molds require regular maintenance to ensure they continue to perform correctly, adding to the overall cost and complexity of the process.

Cooling and Cycle Time
Cooling is a critical step in the injection molding process, and it can also be a bottleneck. Parts that are large or have thick walls require longer cooling times, which can extend the cycle time and reduce overall efficiency. Optimizing the cooling process is essential to maintaining production speed and part quality.
Preocupaciones medioambientales
Although injection molding generates minimal waste, the process still consumes significant amounts of energy and raw materials. The use of non-renewable plastics also raises environmental concerns. Addressing these issues through material recycling, energy-efficient machines, and sustainable practices is becoming increasingly important in the industry.
Industry Applications of Injection Molding Services
Injection molding services are used across a wide range of industries, each with its specific requirements and challenges.
Industria del automóvil
The automotive industry relies heavily on injection molding to produce a variety of components, from dashboard panels to exterior trim and engine parts. The precision and efficiency of injection molding ensure that these parts meet the stringent safety and performance standards required in the automotive sector.
Interior Components: Injection molding is used to produce interior components such as dashboards, door panels, and center consoles. These parts must be durable, aesthetically pleasing, and meet strict safety standards.
Engine Parts: Injection molding is also used to produce various engine parts, including housings, gaskets, and seals. These parts must withstand high temperatures and pressures, making material selection critical.
Productos sanitarios
The medical device industry demands the highest levels of precision, safety, and reliability. Injection molding services are essential for producing components that meet these stringent requirements.
Surgical Instruments: Injection molding is used to produce surgical instruments that must be biocompatible, sterile, and precise. Materials like medical-grade stainless steel and high-performance polymers are commonly used.
Diagnostic Equipment: Injection molding is used to create components for diagnostic equipment, ensuring they meet the high standards required for medical use.
Implants: Medical implants, such as joint replacements, are often produced using injection molding due to the process’s ability to create parts with precise dimensions and high-quality finishes.
Electrónica de consumo
The consumer electronics industry relies on injection molding for producing components that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing. From smartphone housings to wearable devices, injection molding provides the precision and quality needed to meet consumer expectations.
Smartphone Housings: Injection molding is used to produce smartphone housings, ensuring they are durable, lightweight, and have a high-quality finish.
Wearable Devices: The growing market for wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, depends on injection molding for the production of compact, intricate components.
Connectors and Plugs: Injection molding is also used to produce the small, detailed components required for connectors and plugs, ensuring reliable performance.
Industria aeroespacial
The aerospace industry requires parts that are lightweight, durable, and capable of withstanding extreme conditions. Injection molding is used to produce a variety of components that meet these demanding specifications.
Interior Panels: Injection molding is used to produce interior panels for aircraft, which must be lightweight, durable, and fire-resistant.
Seals and Gaskets: Aerospace components often require seals and gaskets that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Injection molding provides the precision needed to produce these critical parts.
Engine Components: Injection molding is also used to produce various engine components, ensuring they meet the rigorous performance standards required in the aerospace industry.
Packaging Industry
Injection molding is a key process in the packaging industry, where it is used to produce a wide range of containers, lids, and other packaging components.
Bottles and Caps: Injection molding is used to produce bottles and caps for the food and beverage industry, ensuring they are both durable and tamper-proof.
Custom Packaging: The ability to create custom shapes and designs makes injection molding ideal for producing unique packaging solutions that stand out on the shelf.
Sustainable Packaging: With the growing demand for sustainable packaging solutions, injection molding is increasingly used to produce packaging made from biodegradable or recycled materials.
The Future of Injection Molding Services
As technology continues to evolve, the future of injection molding services looks promising. Several key trends are expected to shape the industry in the coming years.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is becoming a major focus in the manufacturing industry, and injection molding is no exception. The development of biodegradable plastics, increased use of recycled materials, and energy-efficient machines are all contributing to a more sustainable injection molding process.
Materiales avanzados
The use of advanced materials, such as high-performance polymers, composites, and nanomaterials, is expected to increase. These materials offer enhanced properties, such as greater strength, lighter weight, and improved resistance to heat and chemicals, making them ideal for demanding applications.
Automatización e Industria 4.0
The integration of automation and Industry 4.0 technologies into injection molding services is expected to drive further improvements in efficiency and quality. Automated systems can handle tasks such as material handling, part inspection, and quality control, allowing for continuous operation and reduced labor costs.
Hybrid Manufacturing
The combination of injection molding with other manufacturing processes, such as additive manufacturing (3D printing), is expected to increase. This hybrid approach allows for the production of complex parts with reduced material waste and improved design flexibility.
Customization and Personalizatio
The growing demand for customized and personalized products is expected to drive the development of new injection molding techniques that allow for greater design flexibility and shorter lead times. This trend is particularly important in industries like consumer electronics and medical devices, where product differentiation is key.
Conclusión
Injection molding services are an essential part of modern manufacturing, providing the precision, efficiency, and scalability needed to produce high-quality parts across various industries. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of injection molding will only grow, driving further innovation and enabling manufacturers to meet the demands of an increasingly competitive market. Whether you’re producing automotive components, medical devices, or consumer electronics, injection molding services offer the flexibility and reliability needed to bring your products to life.