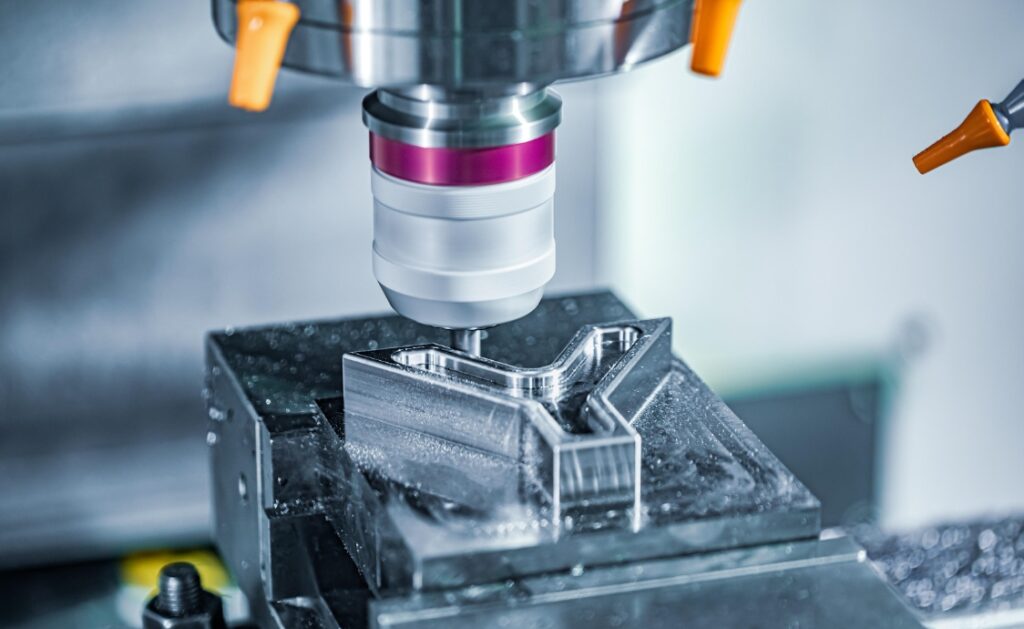
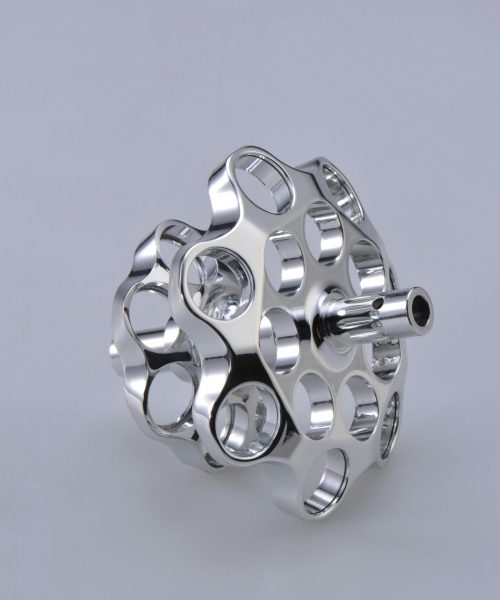
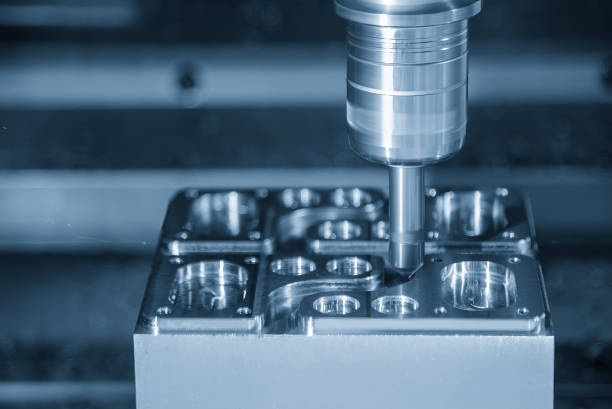
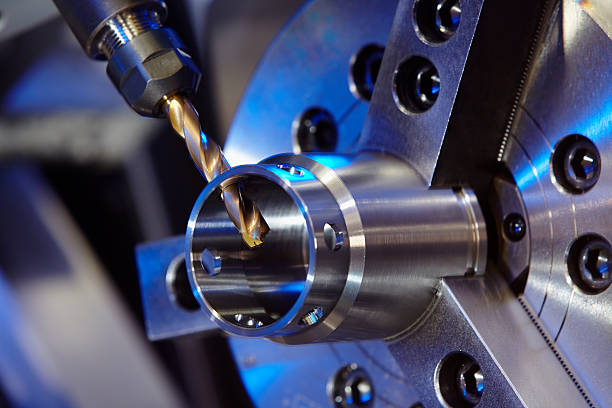
CNC precision machining is essential for producing highly accurate parts for various applications such as automotive components, medical implants, and defense equipment parts. These applications often require tight tolerances as low as ±0.001 inches, which standard machining methods cannot achieve. CNC precision machining utilizes advanced machines and tooling to deliver these precise parts across industries.
To fully leverage this manufacturing precision, it’s crucial to understand its nuances. This article delves into the process, equipment, materials, advantages, and applications of CNC precision machining.

What is CNC Precision Machining?
CNC precision machining is a computer-controlled process that automates material removal based on digital designs and instructions. This automation enables tighter tolerances than conventional machining methods, typically achieving tolerances of ±0.1 to 0.2 mm. Specialized machining tools, optimized parameters, and expert handling are key strategies for achieving this precision.
The primary importance of CNC precision machining lies in producing identical parts for various industries, including automotive, medical, and defense sectors. Multiple pieces of equipment, such as milling machines, EDM setups, and lathes, are used to produce these precision machined parts.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) play crucial roles in this process. CAM converts the 3D model of parts into machining instructions for the CNC machine, dictating all cutting tool movements to create the desired shape.

Step-by-Step Guide to the CNC Precision Machining Process
Design and CAD Modeling Engineers create detailed 3D designs containing dimensions, tolerances, features, scales, and other information using software like AutoCAD or Solidworks. Design for manufacturability (DMF) ensures the model is compatible with precision CNC machining techniques.
CAM and CNC Programming CAM software generates instructions for tool movements based on the CAD model, known as G&M codes. These codes are read by CNC precision machines. The CAM can also simulate optimal tool trajectories, minimizing errors and improving precision.
Setup of CNC Machine Precise CNC machine setup involves tool setup and work holding. The operator installs the tool in the holder and the workpiece on the machine bed or chuck. An Automatic Tool Changing (ATC) mechanism may also be used.
Machining the Part The machine processes instructions for operation. The CNC operator sets parameters like spindle speed, depth, and feed rate. The machine then performs the machining. Testing and fine-tuning parameters ensure parts meet precision requirements.

Post-Processing and Finishing The final step involves removing tool marks, burrs, or chips that affect dimensional accuracy and aesthetics. Post-processing methods like grinding and deburring ensure precise dimensions. Finishing methods like sandblasting, electroplating, or polishing enhance surface quality.
Types of Precision CNC Machines
CNC Milling Machines CNC milling machines involve a rotating cutting tool that moves along multi-axis linear and rotational motions. The spindle can rotate at high speeds (up to 2400 rpm), achieving precision as low as ±0.0025mm. They are ideal for manufacturing complex parts from flat and plane workpieces.
CNC Turning and Lathes CNC lathes or turning centers rotate the workpiece while the tool moves linearly to remove material. They are used to manufacture axially symmetrical items, such as cylindrical products. Precision CNC turning crafts intricate details and shapes.
CNC Drilling Machines CNC drilling machines involve a rotating drill bit and a stationary workpiece. The drill bit penetrates the surface, creating holes. Techniques like spot drilling and peck drilling ensure precision for different materials.

Electrical Discharge Machines (EDM) EDM is a non-contact process that uses electric sparks to erode material, suitable for hard metals and intricate shapes. EDM machines create precise cuts with minimal mechanical stress.
CNC Plasma Cutting Machines CNC plasma cutters use a beam of ionized gas to cut thermally conductive materials. Plasma cutting offers exceptional machining precision with tolerances as low as 0.001 inches.
CNC Precision Grinding Machines CNC grinders use a rotating abrasive wheel to remove surface imperfections and smooth surfaces. These machines provide polished or mirror-like finishes with roughness values of 3.2 to 0.8 μm.
Materials Suitable for CNC Precision Machining
Metals Metals like aluminum, steel, stainless steel, titanium, copper, brass, bronze, Inconel, and Monel are commonly used. The hardness of metals demands diamond-coated carbide tools and efficient cooling systems to counter heat buildup.
Plastics Plastics like Nylon, ABS, Polycarbonate, Polyethylene, POM, PTFE, PEEK, and Acrylic are used. Plastic machining requires slower production speeds due to heat sensitivity.
Key Applications and Industries of CNC Precision Parts
Automotive Custom parts and prototypes such as engine components, transmission parts, and custom dashboards.
Aerospace Components with critical tolerance requirements like turbine blades, landing gear parts, and satellite components.
Medical Devices requiring high precision such as surgical instruments, custom orthopedic implants, and diagnostic equipment parts.
Electronics Compact and precise components like PCB enclosures, heat sinks, and custom sensor housings.

Advantages of High Precision CNC Machining
Increased Accuracy and Repeatability CNC precision machining ensures tight precision and consistency across batches, producing identical parts in large volumes.
Reduced Waste and Enhanced Efficiency Optimal tools and parameters maximize material use and minimize waste, reducing material costs and improving production efficiency.
Complex Geometries with Tight Tolerances Multi-axis capabilities and computer-controlled tooling allow for highly complex parts and precision machined products.
Material Versatility CNC machining accommodates various materials, providing flexibility in choosing the best-fit material for specific applications.
Flexibility in Production CNC precision machining techniques are flexible with production volume, suitable for both prototypes and large-scale runs.
Choosing a CNC Precision Machining Partner
Selecting a reliable precision machining partner involves evaluating their technical capabilities and industry experience. Ensure they have the necessary CNC machines and quality control equipment to meet your requirements.
GCH Process is a China-based precision CNC machining company with extensive experience in various industries. We offer precise CNC machining services with tolerances as low as 0.002 inches.
Features of Our Services:
- Multi-axis CNC machines (3, 4, and 5)
- Advanced EDM and CNC plasma cutters
- Expert engineers and operators
- Rigorous quality control and ISO 9001 or AS9100 certifications
- Prototyping and small batch runs with flexible scalability options
- 100+ material options
- Client-centric communication and rapid lead times

Conclusion
CNC precision machining addresses the complexity and dimensional accuracy required in modern manufacturing. The automation and minimal human intervention in CNC operations allow for stringent tolerances, speed, efficiency, and customization, reducing time and costs.
Choosing the right CNC precision machining partner is essential for leveraging these benefits. GCH Process offers the expertise and capabilities to meet diverse manufacturing needs, ensuring high-quality, precise parts for various applications.
FAQs
What is the difference between CNC machining and precision machining? CNC machining automates tool movements via computer programs, while precision machining focuses on achieving tight tolerances and high accuracy.
How accurate is CNC machining? CNC machining can achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.001 inches (±0.025 mm) or better, depending on the machine’s capabilities and the workpiece material.
What are the types of CNC precision machines? Common types include CNC milling machines, lathes, routers, EDMs, plasma cutters, CNC laser cutters, and grinders.
What is CNC precision machining used for? It’s used for manufacturing high-accuracy components in industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and defense.
Is CNC precision machining expensive? It can be relatively expensive due to its advanced technology and high accuracy, but the efficiency and speed reduce per-part costs in the long run.